Aktualitäten 2019
« ZURÜCK
 Feuerwerke
Feuerwerke
 Schlüssel zur Robustheit von Pflanzen entdeckt
Schlüssel zur Robustheit von Pflanzen entdeckt
 Mit Gift der Kegelschnecken zur Schmerzlinderung
Mit Gift der Kegelschnecken zur Schmerzlinderung
 Atombilder zeigen ungewöhnlich viele Nachbarn für einige Sauerstoffatome
Atombilder zeigen ungewöhnlich viele Nachbarn für einige Sauerstoffatome
 Wie ein Molekül das Klima verändern kann
Wie ein Molekül das Klima verändern kann
 Bioprinting: Lebende Zellen im 3D-Drucker
Bioprinting: Lebende Zellen im 3D-Drucker
 Neues Verfahren zur schnelleren und einfacheren Herstellung lipidierter Proteine
Neues Verfahren zur schnelleren und einfacheren Herstellung lipidierter Proteine
 Wie schnell Elektronenspins tanzen
Wie schnell Elektronenspins tanzen
 2.000 Atome an zwei Orten gleichzeitig
2.000 Atome an zwei Orten gleichzeitig
 Künstliche Intelligenz bringt Licht ins Dunkel
Künstliche Intelligenz bringt Licht ins Dunkel
 Das Trojanische Pferd im Molekül
Das Trojanische Pferd im Molekül
 Verborgene Seiten der Kristalle sichtbar machen
Verborgene Seiten der Kristalle sichtbar machen
 Atom-Manipulationen spielerisch entdecken
Atom-Manipulationen spielerisch entdecken
 Neue Erkenntnisse könnten Solarzellen günstiger machen
Neue Erkenntnisse könnten Solarzellen günstiger machen
 Wie man Nanoteilchen nach ihrer ’Form’ trennen kann
Wie man Nanoteilchen nach ihrer ’Form’ trennen kann
 Krebsmedikament wird durch langsame Elektronen aktiviert
Krebsmedikament wird durch langsame Elektronen aktiviert
 Wenn Elektronen mittanzen dürfen
Wenn Elektronen mittanzen dürfen
 Ketone umweltfreundlich erzeugen
Ketone umweltfreundlich erzeugen
 Batterieforschung an der TU Graz: Neue Forschungserfolge auf dem Weg zur Super-Batterie
Batterieforschung an der TU Graz: Neue Forschungserfolge auf dem Weg zur Super-Batterie
Chemie
Ergebnisse 1 - 20 von 27.
Chemie - 18.12.2019

Farbenprächtige Feuerwerke signalisieren nicht nur den Jahreswechsel, sondern erzeugen auch besonders viel so genannten Ultrafeinstaub, also Partikel mit einem Durchmesser von weniger als 0,1 Mikrometer. Dadurch erhöht sich die Konzentration von bestimmten chemischen Elementen in der Luft rund um Silvester deutlich, wie zwei Chemiker der Universität Graz nachgewiesen haben.
Biowissenschaften - Chemie - 04.12.2019
FWF etabliert neuen Spezialforschungsbereich zum Thema RNA-Modifikationen
Der Fonds zur Förderung der wissenschaftlichen Forschung (FWF) etabliert einen neuen Spezialforschungsbereich namens RNA-DECO. Mit einem Gesamtvolumen von über vier Millionen Euro werden in den kommenden vier Jahren insgesamt 12 Forschungsgruppen gefördert, die sich mit der chemischen Modifikation von Ribonukleinsäure (RNA) befassen.
Biowissenschaften - Chemie - 28.11.2019

Forschende vom Austrian Centre of Industrial Biotechnology (acib) und TU Graz entschlüsselten gemeinsam den Mechanismus der Apiose-Biosynthese - die Basis zur Herstellung von Zuckermolekülen für neue Feinchemikalien oder Biopharmazeutika. Ob Wind oder Wetter - Um vor Umwelteinflüssen geschützt zu sein, müssen Pflanzen gleichzeitig robust und biegsam sein.
Biowissenschaften - Chemie - 04.11.2019

ForscherInnen nutzen Conotoxine für neue Ansätze bei der Schmerztherapie Unter den Naturstoffen mit großem Potenzial für neue Wirkstoffe nehmen Conotoxine eine zentrale Rolle ein. Conotoxine sind strukturierte Peptide aus einem Nervengift, welches Kegelschnecken zum Beutefang und zur Abwehr von Feinden produzieren.
Chemie - Physik - 21.10.2019

Das Identifizieren neuer chemischer Bindungen ist entscheidend für das Entwickeln neuer Materialstrukturen. PhysikerInnen um Jani Kotakoski an der Universität Wien und Jannik Meyer von der Universität Tübingen haben unerwartete, neue Konfigurationen von Sauerstoff und Stickstoff in Graphen entdeckt.
Umwelt - Chemie - 21.10.2019

Wolken entstehen aus Wassertröpfchen, die sich um Aerosolpartikel in der Atmosphäre bilden. Luftschadstoffe tragen zur Entstehung dieser Aerosole wesentlich bei. Nun haben Wissenschaftler aus Frankreich, Japan und Österreich im Labor einen bisher völlig unbekannten Prozess entdeckt: Die Bildung von Aerosolen wird in ihrer frühen Phase durch die Gegenwart von Pyridinium-Ionen befördert.
Materialwissenschaft - Chemie - 21.10.2019

Mit einem neuen Verfahren der TU Wien lassen sich lebende Zellen in feine Strukturen aus dem 3D-Drucker einbauen - extrem schnell und hochausflösend. Wie sich Zellen verhalten und wie neues Gewebe entsteht, lässt sich besonders gut steuern und untersuchen, wenn man die Zellen in ein feines Gerüst einbettet.
Biowissenschaften - Chemie - 11.10.2019

An der TU Graz und Uni Wien entwickelte Methode führt zu besserem Verständnis natürlicher Proteinveränderungen und zur Verbesserung von Proteintherapeutika. Manche körpereigenen Proteine bestehen nicht nur aus Aminosäuren, sondern sind auch mit fettartigen Lipidketten dekoriert, die die biologischen Funktionen des Proteins maßgeblich beeinflussen.
Chemie - Physik - 04.10.2019

ChemikerInnen untersuchen Wechselwirkung von Metallverbindungen und Licht Metallverbindungen zeigen ein faszinierendes Verhalten in ihrer Wechselwirkung mit Licht, was zum Beispiel in Leuchtdioden, Solarzellen, Quantencomputern und sogar in der Krebstherapie angewendet wird. In vielen Fällen spielt dabei der Elektronenspin, eine Art Eigendrehung der Elektronen, eine besondere Rolle.
Physik - Chemie - 23.09.2019

Das Prinzip der Quantenüberlagerung wurde in einer neuen Studie von Wissenschaftlern der Universität Wien in Zusammenarbeit mit der Universität Basel, in einem bisher unerreichten Maßstab getestet. Heiße, komplexe Moleküle bestehend aus fast zweitausend Atomen wurden in eine Quantenüberlagerung gebracht und interferiert.
Chemie - Biowissenschaften - 11.09.2019

ForscherInnen entwickeln um ein Vielfaches schnellere photodynamische Simulationen Die Vorhersage von durch Licht ausgelösten molekularen Reaktionen ist bis dato extrem rechenaufwendig. Ein Team um Philipp Marquetand von der Fakultät für Chemie der Universitäten Wien hat nun unter Nutzung von künstlichen neuronalen Netzen ein Verfahren vorgestellt, welches die Simulation von photoinduzierten Prozessen drastisch beschleunigt.
Chemie - Pharmakologie - 27.08.2019

Einem Forschungsteam um Nuno Maulide von der Fakultät für Chemie der Universität Wien gelang in Zusammenarbeit mit dem Forschungszentrum für Molekulare Medizin (CEMM) der ÖAW die Entwicklung eines eigentlich als Naturstoff vorkommenden modifizierten Wirkstoffs, der künftig in der Medikamentenentwicklung als Immunsupressivum verwendet werden könnte.
Physik - Chemie - 25.07.2019

ForscherInnen entwickeln technologische Tricks zur 3D-Analyse von Kleinstkristallen Um 3D-Kristallstrukturen zu bestimmen, müssen ForscherInnen die Kristalle von allen Seiten durchleuchten können. Sehr kleine Kristalle mit weniger als einem Mikrometer Kantenlänge können dabei nur mittels Elektronenstrahlen untersucht werden.
Physik - Chemie - 08.07.2019

Online-Simulationsspiel macht Graphenforschung der Öffentlichkeit zugänglich Mithilfe eines hochmodernen Elektronenmikroskops kann das Team um Toma Susi an der Universität Wien stark gebundene Materialien Atom für Atom genau manipulieren. Die Messinstrumente des UltraSTEM sind vollständig computergesteuert, so dass eine Simulation die Arbeitsweise der ForscherInnen realitätsgetreu wiedergeben kann.
Physik - Chemie - 25.06.2019

"On-the-fly" maschinelles Lernen erkennt atomare Wechselwirkungen in komplexen Materialien Auf atomarer Ebene können Materialien eine reiche Palette an dynamischem Verhalten zeigen, das sich direkt auf ihre physikalischen Eigenschaften auswirkt. Seit vielen Jahren versuchen WissenschafterInnen diese Dynamik in komplexen Materialien bei verschiedenen Temperaturen zu beschreiben.
Chemie - Physik - 07.06.2019

PhysikerInnen entwickeln neue Strategie zum Trennen von Molekülen In unserem täglichen Leben sind Zweck und Funktion eines Gegenstandes entweder durch dessen Material bestimmt oder durch dessen Form. Ein Regenmantel ist aus wasserabweisenden Stoffen hergestellt, ein Rad immer rund, damit es rollen kann.
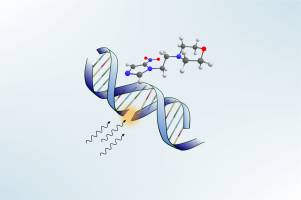
Gesundheit - Chemie - 04.06.2019

In der Strahlentherapie werden verschiedene Moleküle erprobt, um die Wirkung der Strahlung auf Krebszellen zu verbessern. Forscher um Stephan Denifl von der Universität Innsbruck beobachteten nun, dass langsame Elektronen von Nimorazol-Molekülen äußerst effektiv eingefangen werden. Dieses Ergebnis kann eine Erklärung für die selektive Wirkung dieses in der Strahlentherapie bereits eingesetzten Wirkstoffs liefern.
Chemie - Physik - 31.05.2019

Forscher zeigen Möglichkeiten polarisierbarer Simulationen bei ionischen Flüssigkeiten auf Ionische Flüssigkeiten haben besondere Eigenschaften, die sie für viele Anwendungen interessant machen. Je nach Kombination von Anionen und Kationen können die flüssigen Salze z.B. sehr wasser(un)löslich, leitfähig oder temperaturstabil sein.
Chemie - Pharmakologie - 27.05.2019

ChemikerInnen der Universität Wien entwickeln neue Synthesemethode Neue Methoden zu finden bildet in der organischen Synthese die Grundlage für Fortschritte in der pharmazeutischen Wirkstoffentwicklung, der Materialwissenschaft sowie der chemischen Biologie und spielt somit eine zentrale Rolle in unserem Alltag.
Materialwissenschaft - Chemie - 25.04.2019

TU Graz-Forscher entdeckt erstmals Mittel zur Unterdrückung von Singulett-Sauerstoff in Lithium-Sauerstoff-Batterien, um deren Lebensdauer zu verlängern. Weiteres Bildmaterial zum Download am Ende der Meldung . Seit 2012 arbeitet Stefan Freunberger am Institut für Chemische Technologien von Materialien der TU Graz an der Entwicklung einer neuen Batteriegeneration, die leistungsfähiger, langlebiger und in ihrer Herstellung kostengünstiger ist als derzeitige Modelle.
